Exploring the Knowledge Structure and Thematic Evolution of NTIS-Related Research in South Korea (2008-2024): A Bibliometric Analysis

Byung-Hwan Hyun (Department of Business Consulting, Daejeon University, Daejeon, Korea)

Abstract
This study represents the first systematic analysis of research related to the National Science & Technology Information Service (NTIS)—South Korea’s comprehensive national Research and Development (R&D) information portal—from 2008 to 2024, utilizing bibliometric analysis, thematic analysis, and selective literature review. The study aims to identify key research trends, collaborative patterns, and thematic evolution in NTIS-related research to understand its knowledge structure and provide directions for scholarly and system development. The analysis reveals that despite limited publications (169 articles), NTIS research demonstrates steady growth with 13.9% annual growth. Distribution analysis using Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) indicates low concentration levels across authors, institutions, and journals, though citations show higher concentration. Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information (KISTI) leads in all performance indicators and serves as the central hub in interinstitutional collaboration networks. Research scope has expanded into diverse academic fields, with growth in interdisciplinary studies, business administration, and engineering. While studies using NTIS data have increased, research on system improvement has declined. Thematic evolution analysis reveals nine research clusters and shows a shift from system development towards R&D trend analysis, performance evaluation, and advanced analytical methodologies, including Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies. Major research themes include NTIS system implementation, data quality management, R&D investment-performance analysis, economic impact assessment, and analytical techniques. This study indicates that NTIS’s function is evolving beyond R&D information service into a data-driven academic analysis infrastructure supporting evidence-based knowledge production across disciplines. To address limited research volume and domestic concentration, this study recommends activating NTIS-related academic communities, expanding international participation through compatibility with global systems, and building an intelligent platform for customized services.
- keywords
- National Science & Technology Information Service (NTIS), bibliometric analysis, research trends, thematic evolution, selective literature review
1. INTRODUCTION
Science and Technology (S&T) information systems are increasingly important as critical infrastructure for the production, sharing, and utilization of knowledge within national Research and Development (R&D) ecosystems. By integrating research information, these systems enhance national innovation capabilities, support the efficient allocation of resources, and provide critical evidence for R&D policy decisions (Oh, 2008; Won et al., 2023). Major countries operate comparable R&D information services that reflect their policy environments and institutional structures to enhance public R&D investment efficiency and strengthen performance management. The United States operates the Research Portfolio Online Reporting Tools, Expenditures, and Results (RePORTER), the European Union (EU) maintains the Community Research and Development Information Service (CORDIS), and Japan administers the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research Database (KAKEN).
In South Korea, the National Science & Technology Information Service (NTIS)—a comprehensive knowledge portal providing lifecycle information on national R&D activities—was established in 2008 to manage information across the entire national R&D lifecycle (Korea Institute of Science and Technology Evaluation and Planning [KISTEP], 2013). NTIS has contributed to improving investment efficiency and research productivity by systematically linking data from R&D planning to outcome dissemination (KISTEP, 2025; Park, 2018). Recently, it has evolved into an intelligent platform leveraging big data and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies, thereby playing a critical role in enhancing South Korea’s S&T innovation and global competitiveness (Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information [KISTI], n.d.; Lee & Yang, 2021; Lee et al., 2020). Alongside this expanding role of NTIS, the active promotion of NTIS utilization within South Korea’s national R&D ecosystem and its enhanced role as a central national S&T information platform have led to an increasing trend of conducting analyses based on NTIS data, resulting in the steady expansion of NTIS-related research.
However, despite this clear growth in activity, a significant research gap remains: No comprehensive and systematic analysis has been conducted to date that maps the research trends, traces the evolution of academic collaboration networks, or identifies the major thematic areas within this body of NTIS-related studies. This limitation hinders a holistic understanding of the knowledge production dynamics and impact patterns specific to this research area, thereby limiting the ability to derive meaningful insights that could advance scholarly research focused on NTIS itself or enhance the broader utilization of NTIS-based data.
To address this deficiency, this study undertakes a multi-faceted analysis. We employ bibliometric and network analyses specifically to uncover the underlying knowledge structures and collaborative relationships that have formed within this research area. Concurrently, thematic analysis and selective review are utilized to identify key research topics and track their thematic evolution over time, thereby fostering an understanding of the research area’s qualitative growth and informing future research directions. This analytical approach provides insights beyond mapping the research landscape; it offers valuable insights into the broader socio-informational impacts of a national R&D information system like NTIS on its academic ecosystem, particularly concerning knowledge influence and scholarly concentration versus diversity. This case analysis of South Korea’s NTIS furnishes transferable policy and practical implications for other countries currently in the process of developing or enhancing similar R&D information infrastructures.
This study systematically examines the knowledge structure and major research themes through bibliometric analysis, network analysis, thematic analysis, and literature review of NTIS-related research literature from 2008 to 2024. This study addresses the following research questions:
■ RQ1: How have knowledge production and impact in NTIS-related research evolved over time? This study analyzes temporal patterns in published studies to identify these trends.
■ RQ2: To what extent do disparities exist among research entities in publication and citation performance? This study assesses concentration in publications and citations across authors, institutions, and journals.
■ RQ3: Which research entities lead NTIS-related studies? This work identifies prominent authors, institutions, and journals based on publication volume and citation impact.
■ RQ4: How are collaborative relationships formed among institutions? This study analyzes institutional collaboration networks and key players driving inter-organizational cooperation.
■ RQ5: What themes characterize NTIS-related research, and how have they evolved? This study identifies major research themes through keyword analysis, academic field analysis, and thematic clustering, and explores their contextual meaning and development through literature review.
2. NTIS: DEVELOPMENT AND COMPARISON
2.1. Background and Development of NTIS in South Korea
The NTIS of South Korea, established in 2008, serves as a knowledge portal providing lifecycle information on national R&D activities, spanning planning, implementation, performance evaluation, and outcome dissemination (KISTEP, 2013; Kwak et al., 2022). Under the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), the KISTI has led NTIS development to strengthen national R&D competitiveness by integrating scientific information across government departments and institutions (KISTI, n.d.). KISTI’s responsibilities include maintaining the NTIS system, establishing data linkage frameworks between departments and institutions, managing data quality, improving services based on user needs, and advancing services through emerging technologies (KISTI, 2019). KISTI has improved the NTIS system through data quality enhancement, user-centered functionality, and analytical capability development (Lee & Yang, 2021). NTIS is pursuing service advancement through intelligent service provision using big data analysis and AI technologies (KISTEP, 2025; Lee et al., 2020). As of January 2025, NTIS collaborates with 18 specialized government agencies that oversee R&D programs to collect research outcome data. The system supports over 22,000 registered users and provides access to more than 1.15 million project data entries, serving as a hub for national R&D information in South Korea (KISTI, n.d.).
2.2. Role of NTIS in National R&D Ecosystem
NTIS functions as a cornerstone of South Korea’s national R&D ecosystem, delivering services across the R&D lifecycle, and serves within the national research data governance framework (KISTEP, 2025; Kwak et al., 2022; Lee & Yang, 2021). It provides integrated access to information—encompassing national R&D programs, projects, researchers, facilities, equipment, and research outcomes—enabling stakeholders to make evidence-based decisions (KISTI, n.d.; Lee & Kim, 2021; Shmagun et al., 2022; Won et al., 2023). NTIS enhances efficiency through multiple mechanisms: preventing redundant project investments, encouraging shared utilization of research infrastructure, enabling performance verification, and ensuring transparent dissemination of R&D information (KISTEP, 2025; KISTI, n.d.). It promotes the practical application and impact of research by increasing the accessibility of R&D outcomes. The economic contributions of NTIS are substantial, generating multiplier effects that stimulate production, create added value, and promote job growth within the South Korean economy (Huh et al., 2009; Park, 2018; Park et al., 2012). From a policy standpoint, NTIS enhances transparency in national R&D investments and facilitates evidence-based policy formulation (KISTEP, 2025; Won et al., 2023). This data-driven approach improves science policies by providing information for evaluating researchers and institutions, identifying promising technological areas, and informing R&D budget allocation. Beyond domestic contributions, NTIS has expanded its international cooperation since the mid-2010s, collaborating with Costa Rica, Belarus, and Vietnam to establish S&T information systems and improve R&D information management capabilities (KISTI, n.d.).
2.3. Comparison with Major International Systems
Major countries operate national R&D information systems reflecting their policy environments and institutional structures to enhance public R&D investment efficiency and strengthen performance management (KISTEP, 2013; KISTI, n.d.; Won et al., 2023).
The United States operates the RePORTER system, managed by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), to transparently disclose the status and outcomes of its federal government R&D investments and enhance public access. This database encompasses research projects funded not only by NIH but also by other major agencies and operating divisions within the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). RePORTER provides integrated information covering the entire research lifecycle, including research objectives, budget details, principal investigators and their affiliated institutions, published papers, patents, and clinical trial results. Users can perform in-depth searches and analyses based on criteria such as diseases, research areas, institutions, and research types. This system serves as a core infrastructure that supports researchers in identifying research trends and discovering collaboration opportunities, and aids policymakers in evaluating R&D investments and formulating strategies (NIH, n.d.). Japan administers the Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (KAKENHI) program through the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) under the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) guidance (JSPS, n.d.). The National Institute of Informatics (NII) operates the KAKEN Database to enhance transparency (NII, n.d.). This system provides data on research projects, including objectives, investigators, institutions, funding amounts, durations, and outcomes. Within the EU, the CORDIS, operated by the European Commission (EC) under the Directorate-General for Research and Innovation (DG RTD), provides information on projects funded by EU programs, including Horizon Europe and Horizon 2020. The platform publishes project descriptions, organizations, funding levels, and deliverables, promoting collaboration within the EU research community (EC, n.d.).
Compared to international systems, South Korea’s NTIS exhibits several distinctive features (Oh, 2008; Shmagun et al., 2022; Won et al., 2023). First, unlike systems focusing on specific funding bodies (e.g., NIH/HHS in RePORTER, KAKENHI in KAKEN) or programs (e.g., EU framework programs in CORDIS), NTIS integrates nationwide information on government-funded R&D activities—including investments, projects, outcomes, researchers, research infrastructure, and technology statistics—across ministries and scientific domains (KISTEP, 2013; KISTI, n.d.). Second, NTIS supports information access across the R&D lifecycle by collecting and linking data from government systems—from project planning and evaluation to execution and utilization (KISTEP, 2025; Lee & Yang, 2021). Third, NTIS is structured to support national R&D policy formulation, strategic budgeting, and performance evaluation by offering integrated data for decision-making (KISTEP, 2025; Won et al., 2023). It thus plays a key role in evidence-based R&D policymaking in South Korea. Lastly, while platforms like CORDIS focus on disseminating research results, NTIS facilitates R&D outcome utilization by linking to technology transfer platforms, industry matching services, and commercialization channels (KISTI, n.d.; Park, 2018). These functions maximize the socio-economic impact of public R&D investments beyond information disclosure. In summary, NTIS serves as a comprehensive platform, playing a central role in South Korea’s R&D ecosystem by providing centralized information, integrating lifecycle data for policy support, and promoting practical utilization of research outcomes.
3. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
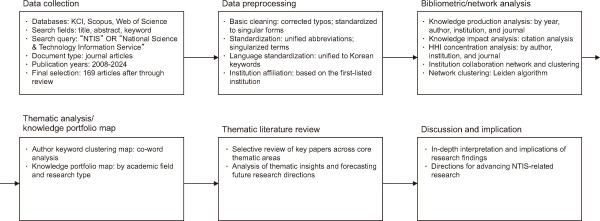
This study applied an integrated research methodology that can be characterized as comprehensive bibliometric analysis combined with thematic analysis and selective review, to systematically examine the knowledge structure and thematic evolution of NTIS-related academic literature. The methodology encompasses data collection and preprocessing, bibliometric analysis, network analysis, concentration analysis, thematic analysis, and targeted literature examination, as shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1
Research framework for analysis. KCI, Korea Citation Index; NTIS, National Science & Technology Information Service; HHI, Herfindahl-Hirschman Index.
Bibliographic data required for the research were collected from the Korea Citation Index (KCI) and international scholarly databases, including Scopus and Web of Science (WOS), on January 5, 2025. The search terms “NTIS” and “National Science & Technology Information Service” were used, targeting the title, abstract, and keyword fields of publications. For KCI, both Korean and English search terms were applied to expand the search scope. The research period was set from 2008, when NTIS was established, to 2024, and only articles published in academic journals were included as analysis targets to ensure data consistency. The initially collected data were thoroughly reviewed for relevance to the research objectives, excluding inappropriate literature, and nine duplicate articles across databases were removed according to priority order (KCI → Scopus → WOS). Considering concerns regarding the credibility of certain Scopus-indexed journals and the limited number of WOS articles, the final analysis was conducted exclusively on 169 articles indexed in KCI.
The following data preprocessing procedures were performed on the final selected 169 articles. Basic cleaning work was conducted, including correcting typographical errors and standardizing plural expressions to singular forms. Author keywords written in both Korean and English were unified into Korean to ensure analytical consistency, and when both full terms and abbreviations were used, such as ‘Research and Development’ and ‘R&D,’ terminology was standardized using abbreviations. Additionally, when multiple institutional affiliations were listed for an author in a paper, the first listed institution was classified as that author’s affiliation.
Based on the preprocessed data, the following analyses were performed.
First, bibliometric analysis was conducted to evaluate the productivity and scholarly impact of NTIS-related research. This method is used to identify trends and key actors in specific research areas through quantitative analysis of bibliographic information from published literature (Donthu et al., 2021; Kim & Park, 2025). In this study, publication patterns by year, performance indicators by author/institution/journal, and citation relationships were analyzed for 169 articles.
Second, concentration analysis using the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) was conducted to measure the concentration of publications and citations among authors, institutions, and journals (Chi, 2016; Hirsch, 2005). The HHI, calculated as the sum of squares of each entity’s market share (HHI=∑(si)2), is an indicator showing whether resources in a specific field are concentrated among a few entities or distributed diversely (Evren et al., 2021). Values below 1,500 were interpreted as low concentration, 1,500-2,500 as moderate concentration, and above 2,500 as high concentration (Carlton & Perloff, 2005).
Third, network analysis based on co-authorship data was conducted to understand inter-institutional collaboration structures. This analysis is effective in visually mapping relationships between research entities and revealing central actors and hidden collaboration patterns within the entire network, particularly in examining how collaboration structures evolve in specific research domains (Hyun et al., 2022). Collaboration networks were constructed targeting institutions that conducted joint research more than twice, and clustering analysis using the Leiden algorithm was applied to identify subgroups within the network (Traag et al., 2019).
Fourth, thematic analysis was performed to analyze the flow and characteristics of research topics. Co-word analysis was conducted on author keywords to visualize connections between research topics, targeting keywords that co-occurred more than twice. To identify dynamic changes in academic fields and research types, a knowledge portfolio map was developed and applied, classifying them into four categories based on occurrence frequency and growth rates: ‘core’ (high frequency/high growth), ‘emerging’ (low frequency/high growth), ‘matured’ (high frequency/low growth), and ‘declining’ (low frequency/low growth) (Lee et al., 2008; Yoon et al., 2018).
Finally, this study employed a selective literature review approach to gain a deeper understanding of NTIS-related research themes. This selective review, also known as a narrative approach or semi-systematic literature review, provides a flexible and comprehensive analysis of studies carefully selected by the authors from key research areas, organizing them thematically to understand research developments and patterns within their broader context (Snyder, 2019). This approach has been widely applied in combination with bibliometric analysis to provide both quantitative insights and qualitative understanding of research areas. To select appropriate literature for each research theme, this study consulted with five doctoral-level experts in technology policy, including two university professors and three researchers from government research institutes.
During the research process, the Bibliometrix R package was utilized for bibliographic information analysis, and Python was used for specific analytical tasks such as network visualization. Generative AI (Claude 3.7 Sonnet or Gemini 2.5 Pro) was employed solely as a tool for language translation assistance and refining textual clarity.
4. RESEARCH RESULTS
4.1. Knowledge Production, Impact, and Collaboration
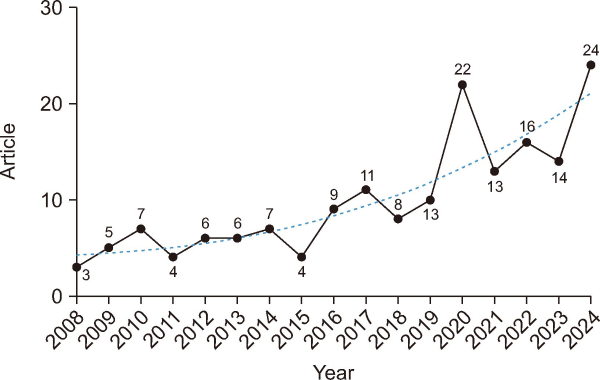
NTIS-related research articles have grown steadily since it was established in 2008. As shown in Fig. 2, initially only three articles were published in 2008, increasing to 11 articles in 2017, 22 articles in 2020, and reaching a peak of 24 articles in 2024. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of NTIS-related research has been 13.9%. In summary, despite its relatively limited number of publications, the field of NTIS-related research has shown long-term growth, albeit with some fluctuations.
Table 1 shows the publication and citation patterns of all articles. The 169 articles received a total of 635 citations, with an average of 3.8±6.7 citations per article. 104 articles (61.5% of 169) were cited at least once, and the most highly cited article accumulated 57 citations. Eighteen papers (10.7%) received 10 or more citations, accounting for 53.1% of total citations. The h-index, which considers both the quantity and quality of papers, was 12, indicating that 12 articles were cited at least 12 times each. The HHI was 245.3, which, according to Carlton and Perloff (2005), does not indicate a high level of concentration.
Table 1
Publication and citation metrics
| Index | Articles (A) | Cited articles (B) | Total citations | Average citations (B/A) | h-index | HHI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 169 | 104 | 635 | 3.8±6.7 | 12 | 245.3 |
Among 391 contributing authors, 235 (60.1%) had at least one citation. The average number of authors per article was 3.0±1.8. The average h-index of authors was 0.7±0.7, indicating that individual scholarly impact is not particularly high. We calculated the HHI to assess concentration levels, resulting in scores of 41.5 for publications and 114.4 for citations. While citation concentration was marginally higher, both HHI scores are low, suggesting a diverse distribution of contributing authors rather than dominance by a few.
Table 2 presents the distribution of leading authors in NTIS-related research based on publication count, citation frequency, and h-index. Among the top contributors by publication, Tae-Hyeon Kim and Byeong-Hee Lee tied for first place, each with 11 articles. In citations, Sangki Jeong, Kyunghwa Kim, and Seokjong Park shared the highest citation count with 57 citations each. Regarding scholarly impact, as measured by the h-index, Byeong-Hee Lee and Jungsun Lim ranked highest, each with an h-index of 4. Three authors—Jae-Soo Kim, Byeong-Hee Lee, and Seunghwan Oh—ranked among the top across all three metrics. Several authors also demonstrated strong performance in both publication and h-index: Kwang-Nam Choi, Sang-Kuk Kim, Tae-Hyeon Kim, Jungsun Lim, and Myungseok Yang. Across these metrics, a significant number of the authors were affiliated with KISTI, while others were associated with institutions such as Gyeonggi Business & Science Accelerator (GBSA), Gyeongsang National University, Hoseo University, Jeonbuk National University, Korea University, Science and Technology Policy Institute (STEPI), and University of Science and Technology (UST).
Table 2
Leading authors in publications and citations
| Publication | Citation | h-index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank (n, %) | Author | Rank (n, %) | Author | Rank (n) | Author | ||
| 1 (11, 6.5%) | Tae-Hyeon Kim, Byeong-Hee Lee | 1 (57, 9.0%) | Sangki Jeong, Kyunghwa Kim, Seokjong Park | 1 (4) | Byeong-Hee Lee, Jungsun Lim | ||
| 3 (7, 4.1%) | Kwang-Nam Choi, Jungsun Lim | 3 (3) | Kwang-Nam Choi, Ju-Yeon Gang, Jae-Soo Kim, Sang-Kuk Kim, Tae-Hyeon Kim, Yeon-Hwa Nam, Hyo-Jung Oh, Seunghwan Oh, Dongkyu Won, Myungseok Yang | ||||
| 4 (53, 8.3%) | Byeong-Hee Lee | ||||||
| 5 (6, 3.6%) | Myungseok Yang | 5 (50, 7.9%) | Seunghwan Oh | ||||
| 6 (4, 2.4%) | Seoung Hun Bae, Hoekyung Jung, Jae-Soo Kim, Sang-Kuk Kim, Jongwon Lee, Seunghwan Oh, Kang-Ryul Shon, Sanghyuk Suh | 6 (45, 7.1%) | Pilseong Jang | ||||
| 7 (40, 6.3%) | Jae-Soo Kim | ||||||
| 8 (29, 4.6%) | Ki-Suk Choi, Eunsil Kim, Woojung Shim | ||||||
In summary, a diverse group of researchers has contributed to NTIS-related studies, and a significant number of the authors who demonstrated outstanding quantitative and qualitative performance in this study were affiliated with KISTI.
NTIS-related research involved 118 institutions, with an average of 2.3±5.8 publications per institution. Among these institutions, 74.6% (88 institutions) received citations, with an average citation count of 7.8±21.8. The average h-index of all institutions participating in knowledge production was 1.0±1.0, which was not particularly high. The HHI for publications was 611.6 and for citations was 754.7, indicating that while absolute concentration levels were not high, citation concentration was relatively higher than publication concentration.
Table 3 shows the distribution of major institutions in NTIS-related research based on publication, citation, and h-index. Among the top-ranking institutions, KISTI (63 articles), UST (9), and Chungbuk National University/STEPI (8 each) ranked 1-3 in terms of publication. For citations, KISTI (206 citations), STEPI (76), and KISTEP (61) were the top three institutions, while in h-index, KISTI (7) and STEPI/UST (4 each) recorded the highest scores. While KISTI ranked first across all three metrics, Chungbuk National University STEPI and UST also demonstrated high performance, placing within the top ten in each category. Institutions appearing in the top rankings across two metrics include Chungnam National University, Hansung University, Hoseo University, Jeonbuk National University, KISTEP, Konkuk University, Kookmin University, Korea University, and Pukyong National University.
Table 3
Leading institutions in publications and citations
| Publication | Citation | h-index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank (n, %) | Institution | Rank (n, %) | Institution | Rank (n) | Institution | ||
| 1 (63, 37.3%) | KISTI | 1 (206, 32.4%) | KISTI | 1 (7) | KISTI | ||
| 2 (9, 5.3%) | UST | 2 (76, 12.0%) | STEPI | 2 (4) | STEPI, UST | ||
| 3 (8, 4.7%) | Chungbuk National Univ., STEPI | 3 (61, 9.6%) | KISTEP | ||||
| 4 (57, 9.0%) | GBSA | 4 (3) | Chungbuk National Univ., Jeonbuk National Univ. | ||||
| 5 (6, 3.6%) | Jeonbuk National Univ. | 5 (43, 6.8%) | UST | ||||
| 6 (5, 3.0%) | Chungnam National Univ., Korea Univ., Seoul National Univ. | 6 (34, 5.4%) | Chungbuk National Univ. | 6 (2) | Chungnam National Univ., Gumi Univ., Hansung Univ., Hoseo Univ., KISTEP, Konkuk Univ., Kookmin Univ., LX-SIRI, Pukyong National Univ., Semyung Univ. | ||
| 7 (29, 4.6%) | Korea Univ. | ||||||
| 8 (23, 3.6%) | Kookmin Univ., Pukyong National Univ. | ||||||
| 9 (4, 2.4%) | Gyeongsang National Univ., Hanyang Univ., Hoseo Univ., Konkuk Univ., Pai Chai Univ., Sungkyunkwan Univ. | ||||||
| 10 (22, 3.5%) | Hansung Univ. | ||||||
KISTI, Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information; UST, University of Science and Technology; Univ., University; STEPI, Science and Technology Policy Institute; KISTEP, Korea Institute of Science and Technology Evaluation and Planning; GBSA, Gyeonggi Business & Science Accelerator; LX-SIRI, LX-Spatial Information Research Institute.
In summary, research in this field involves participation from diverse institutions, maintaining varied distribution among institutions in both publications and citations. While KISTI significantly leads this research across all metrics, government research institutions (KISTEP, STEPI) and various Korean universities are contributing to knowledge production and impact in this domain.
A total of 96 journals published NTIS-related research, with an average of 1.8±2.3 articles per journal. Among these, 64.6% (62 journals) received citations, with an average citation count of 6.6±18.4. The average h-index across all journals was 0.8±1.0, further indicating a relatively modest level of impact. The concentration of journals was higher in citations than in publications. The HHI was 277.6 for publications and 906.7 for citations.
Table 4 presents the distribution of leading journals in NTIS-related research based on publication, citation, and h-index. The Journal of the Korea Contents Association, and Journal of Korea Technology Innovation Society ranked first and second across all metrics. The Journal of the Korea Contents Association ranked first in article publications (17), second in citations (51), and second in h-index (4). The Journal of Korea Technology Innovation Society ranked second in article publications (15), first in citations (167), and first in h-index (7).
Table 4
Leading journals in publications and citations
| Publication | Citation | h-index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank (n, %) | Journal | Rank (n, %) | Journal | Rank (n) | Journal | ||
| 1 (17, 10.1%) | J. of the Korea Contents Association | 1 (167, 26.3%) | J. of Korea Technology Innovation Society | 1 (7) | J. of Korea Technology Innovation Society | ||
| 2 (15, 8.9%) | J. of Korea Technology Innovation Society | 2 (51, 8.0%) | J. of the Korea Contents Association | 2 (4) | J. of the Korea Contents Association | ||
| 3 (5, 3.0%) | JISTaP, J. of Korea Academia-Industrial Cooperation Society | 3 (32, 5.0%) | J. of the Korean Society for Information Management | 3 (3) | J. of the Korean Society for Information Management | ||
| 4 (30, 4.7%) | J. of the Korea Convergence Society | 4 (2) | J. of Industrial Innovation, J. of Intelligence and Information Systems, J. of Korea Academia-Industrial Cooperation Society, J. of Korean Library and Information Science Society, J. of Korean Society of Archives and Records Management, J. of Technology Innovation, J. of the Korea Convergence Society, Korean J. of Business Administration | ||||
| 5 (4, 2.4%) | J. of Korean Society of Industrial and Systems Engineering, J. of the Korean Society for Information Management, J. of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Technology Engineers | 5 (23, 3.6%) | Innovation Studies | ||||
| 6 (21, 3.3%) | J. of the Korean Society of Hazard Mitigation | ||||||
| 7 (20, 3.1%) | J. of Korea Academia-Industrial Cooperation Society | ||||||
| 8 (3, 1.8%) | J. of Convergence on Culture Technology, J. of Intelligence and Information Systems, J. of the Korea Institute of Information and Communication Engineering, J. of the Korea Society of Computer and Information, J. of the Korean Society for Library and Information Science, J. of the Korean Society of Hazard Mitigation, Korean J. of Business Administration | 8 (19, 3.0%) | Korean J. of Business Administration | ||||
| 9 (18, 2.8%) | J. of Information Technology Applications & Management, J. of Intelligence and Information Systems | ||||||
Following these leading journals, the Journal of Intelligence and Information Systems, Journal of Korea Academia-Industrial Cooperation Society, Journal of the Korean Society for Information Management, and Korean Journal of Business Administration also ranked highly across the metrics. Journals appearing in the top rankings across two metrics include the Journal of the Korea Convergence Society, Journal of the Korean Society for Hazard Mitigation, and Journal of the Korean Society for Library and Information Science.
In summary, a wide range of journals contributed to the dissemination, with citation concentration being relatively higher than publication. Journals related to contents, technology innovation, library and information science, convergence, and business administration led the research in this field.
This study analyzed institutional collaboration patterns and found that, among 169 articles, 81 (47.9%) exhibited collaboration between institutions. Fig. 3 presents a network constructed based on institutions that collaborated with each other more than twice. A clustering analysis identified a total of three collaborative groups.
Fig. 3
Institutional collaboration clustering map. KISTI, Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information; UST, University of Science and Technology; STEPI, Science and Technology Policy Institute; LX-SIRI, LX-Spatial Information Research Institute; KISTA, Korea Intellectual Property Strategy Agency; KEIT, Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology; KFIS, Korea Finance Information Service.
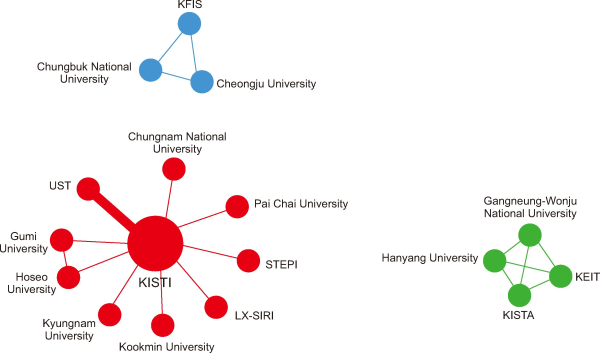
■ Cluster 1 (red): This is the most extensive cluster, with KISTI occupying a central position in the network and demonstrating the highest degree centrality. KISTI maintains close collaborations with nine institutions: Chungnam National University, Gumi University, Hoseo University, Kookmin University, Kyungnam University, LX-Spatial Information Research Institute (LX-SIRI), Pai Chai University, STEPI, and UST.
■ Cluster 2 (green): This cluster consists of Gangneung-Wonju National University, Hanyang University, Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology (KEIT), and Korea Intellectual Property Strategy Agency (KISTA). It reflects collaborations primarily between universities and government R&D-related institutions.
■ Cluster 3 (blue): This is a smaller collaborative group composed of Cheongju University, Chungbuk National University, and Korea Finance Information Service (KFIS).
In summary, nearly half of the NTIS-related studies involve institutional collaboration, with KISTI playing a central role in fostering cooperation between universities and government-funded research institutes.
4.2. Thematic Analysis and Literature Review
For the thematic analysis, we examined the distribution and growth of NTIS-related research across academic fields based on journal classifications provided by the KCI. To ensure consistency in disciplinary categorization, we adopted the sub-discipline level (e.g., business administration or economics within the broader field of social sciences). Considering the distribution of published papers over time, we divided the study period into two phases for comparative analysis: Period 1 (2008-2019, 80 articles) and Period 2 (2020-2024, 89 articles).
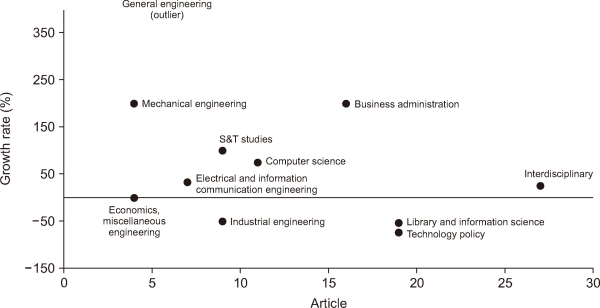
Our analysis identified NTIS-related research across 36 academic fields, expanding from 19 in the earlier period to 31 in the later period. For the 12 major fields (≥2% of total articles), we constructed a knowledge portfolio map based on publication volume and growth rate (Period 2 vs. Period 1), as shown in Fig. 4. In terms of volume, interdisciplinary research leads with 27 articles, followed by technology policy and library and information science (19 each), and business administration (16). In terms of growth rate, general engineering (an outlier) shows the highest increase, followed by business administration and mechanical engineering (both 200.0%), S&T studies (100.0%), and computer science (75.0%). Academic fields were mapped onto a 2×2 matrix: High Growth–High Volume (interdisciplinary research, business administration); High Growth–Low Volume (general engineering, mechanical engineering, S&T studies, computer science, electronic information communication engineering); Low Growth–High Volume (technology policy, library and information science); and Low Growth–Low Volume (industrial engineering, economics, miscellaneous engineering).
In summary, NTIS-related research has significantly expanded in scope over time. While the relative share of technology policy and library and information science is declining, research is increasingly branching into areas such as engineering, computer science, and S&T studies. Interdisciplinary studies and business administration continue to maintain high publication volumes and growth rates, establishing themselves as core research areas.
This study conducted a literature review of major NTIS-related papers in interdisciplinary and business administration fields. While both areas utilized NTIS data to analyze research trends and propose service improvements, interdisciplinary research focused on R&D systems and collaboration strategies, whereas business administration research emphasized the analysis of government R&D investment performance.
An in-depth literature review of interdisciplinary papers revealed three main categories of research topics: (i) Enhancement of NTIS services through improvements in quality, accessibility, and user experience. Shon and Lim (2009) suggested methods to improve R&D data quality, Yu et al. (2020) examined how curation services can improve R&D information accessibility, and Lee et al. (2022) proposed an interactive search system using AI techniques to boost search efficiency. (ii) Analysis of research characteristics and trends in specific fields using NTIS data. Choi et al. (2021), for example, explored the knowledge structure of fuel cell electric vehicles within hydrogen economy projects. (iii) Investigation of R&D collaboration and technology transfer. Kim et al. (2016) studied factors influencing technology transfer in government research institutions, while Min et al. (2024) categorized R&D collaboration models between Korea and developing countries based on innovation performance.
In the realm of business administration, NTIS-related research is also grouped into three main categories: (i) Investigation of R&D characteristics through data and text analysis. Yoo et al. (2020) analyzed national convergence R&D characteristics using NTIS data, and Choi and Lee (2020) identified structural features of regional technology development R&D. (ii) Evaluation of NTIS service quality and usability improvement. Heo and Kim (2020) proposed enhancements to NTIS through an online information service quality evaluation model, and Choi and Son (2022) identified factors influencing the continued use of the NTIS platform based on user surveys. (iii) Analysis of government R&D investment performance and its influencing factors. Ro et al. (2018) empirically assessed government R&D investment performance in industrial technology fields, including patents, technology fee income, and commercialization, while Oh and Park (2020) systematically evaluated the impact of government R&D support for medium-sized enterprises, focusing on asset growth and R&D investment expansion.
Based on input from five doctoral-level experts in technology policy (two university professors and three government research institute researchers), we classified NTIS-related research into three categories: (1) studies analyzing NTIS itself, including its introduction, characteristics, and effects; (2) studies proposing improvements to NTIS; and (3) studies utilizing NTIS or its data. Our analysis revealed that NTIS utilization research dominated the literature (114 articles, 67.5%), followed by NTIS improvement research (47 articles, 27.8%), and NTIS itself research (8 articles, 4.7%). Comparing Period 1 and Period 2, utilization-focused research increased significantly by 42.6%, while NTIS improvement-focused research decreased by 25.9% and research on NTIS itself declined by 66.7%.
To provide more granular insights, we further refined our classification based on expert opinions: NTIS itself was subdivided into NTIS characteristics and NTIS effects; NTIS improvement was categorized into process/system improvement, user usability improvement, data quality improvement, and legal/institutional improvement; and NTIS utilization was classified into R&D trend identification, R&D performance analysis, and R&D applications. We also constructed a knowledge portfolio map (Fig. 5) to visualize these research categories. R&D trend identification (65 articles; 142.1% growth) falls into the High Growth–High Volume quadrant. The High Growth–Low Volume quadrant includes process/system improvement (20 articles; 85.7% growth). R&D performance analysis (33 articles; -26.3%) is positioned in the Low Growth–High Volume quadrant. The Low Growth–Low Volume quadrant encompasses legal/institutional improvement (-83.3%), user usability improvement (-40.0%), NTIS effects/data quality improvement (-100.0%), and NTIS characteristics (0.0%).
Fig. 5
Knowledge portfolio map by research type. NTIS, National Science & Technology Information Service; R&D, Research and Development.
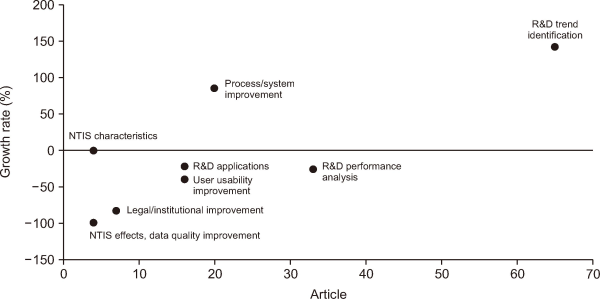
In summary, NTIS-related research has been growing, particularly in studies that utilize NTIS data, with R&D trend identification emerging as a core area. In contrast, research interest has declined in several areas, including legal and institutional improvement and data quality analysis.
This study conducted a literature review on national R&D trend analysis using NTIS data, which has emerged as the most prominent research area. The analysis revealed that research trend analysis is being conducted centered around 10 fields: (i) Health·Medicine·Bio (e.g., Korean medicine, healthcare, women’s health research); (ii) Defense·Disaster Safety·Security (e.g., promising defense technologies, disaster safety response systems); (iii) Energy·Environment (e.g., hydrogen economy, carbon-neutral fuels); (iv) Materials·Components·Equipment (e.g., display materials, membrane materials, optical communication components); (v) ICT·AI·Smart Technologies (e.g., AI, autonomous driving, cloud security); (vi) Content·Cultural Technologies (e.g., immersive media, metaverse, webtoons); (vii) Agriculture·Food (e.g., healing agriculture, food safety, agricultural technology); (viii) Machinery·Equipment (e.g., construction machinery); (ix) Interdisciplinary Fields; and (x) Other Fields (e.g., regional S&T). Among these, research trend analyses in the ICT·AI·Smart Technologies, Health·Medicine·Bio, and Defense·Disaster Safety·Security fields were found to be conducted most actively.
To analyze these research trends, various techniques such as (i) text mining (e.g., graphene technology, agricultural R&D), (ii) topic modeling (e.g., metaverse, AI), (iii) network analysis (e.g., bio-healthcare, disaster safety projects), (iv) patent and citation analysis (e.g., display, all-solid-state batteries), and (v) metadata analysis (e.g., energy technology) have been applied either individually or in combination. The application of topic modeling is showing a significantly increasing trend, and this is projected to continue in the future.
Table 5 shows the changes in top keywords over time based on author keyword frequency. Across all periods, R&D (23 articles) and R&D project (17) were the most frequently appearing keywords. Other frequently observed topics included research methodology terms such as text mining (11), network analysis (9), and topic modeling (7); and R&D lifecycle implementation terms like R&D program (8), R&D investment (7), and R&D performance (6). Furthermore, AI (7) was also a high-ranking keyword, with the literature analysis results showing this comprised papers on AI research trends (5) and the use of AI as an analysis method (2).
Table 5
Leading keywords by period
| Overall (2008-2024) | Period 1 (2008-2019) | Period 2 (2020-2024) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank (n, %) | Keyword | Rank (n, %) | Keyword | Rank (n, %) | Keyword | ||
| 1 (23, 13.6%) | R&D | 1 (8, 10.0%) | R&D program | 1 (16, 18.0%) | R&D | ||
| 2 (17, 10.1%) | R&D project | 2 (7, 8.8%) | R&D | 2 (13, 14.6%) | R&D project | ||
| 3 (11, 6.5%) | Text mining | 3 (5, 6.3%) | R&D performance | 3 (9, 10.1%) | Research trend, Text mining | ||
| 4 (10, 5.9%) | Research trend | 4 (4, 5.0%) | R&D project, R&D information, R&D investment | ||||
| 5 (9, 5.3%) | Network analysis | 5 (8, 9.0%) | Network analysis | ||||
| 6 (8, 4.7%) | R&D program | 6 (7, 7.9%) | AI | ||||
| 7 (7, 4.1%) | AI, R&D investment, Topic modeling | 7 (3, 3.8%) | Data cleansing, DEA, Database integration, GRI, Information quality, IPR, Ontology, Technology transfer | 7 (6, 6.7%) | Topic modeling | ||
| 8 (4, 4.5%) | Deep learning | ||||||
| 9 (3, 3.4%) | Big data, Cluster analysis, LDA, Machine learning, R&D investment, R&D support, S&T standard classification | ||||||
| 10 (6, 3.6%) | R&D performance | ||||||
A comparison of these top keywords by period reveals shifts in research focus and methodology application. In Period 1, R&D lifecycle terms such as R&D program/project and R&D information/investment/performance were the most prominent, followed by terms related to NTIS system development, including database integration, data cleaning, ontology, and information quality. In Period 2, which covers the most recent five years, the focus shifted slightly, with terms related to the R&D lifecycle—such as R&D, R&D projects, and R&D investment/support—remaining prominent. At the same time, new research trend areas emerged among the top keywords, alongside data- and text-analysis methods such as big data, text mining, network analysis, topic modeling, cluster analysis, and Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA). AI-related terms, including machine learning and deep learning, have also gained increased attention as key research topics.
In summary, keywords related to the R&D lifecycle have remained central throughout all periods as core NTIS terms. Meanwhile, the prominence of system development issues, which were important in earlier stages, has decreased. However, various analysis techniques for NTIS, and the application of advanced AI techniques, are emerging as key keywords.
Fig. 6 visualizes the results of network and clustering analysis based on author keywords that co-occurred more than twice in all articles. Through this analysis, nine clusters were identified.
Fig. 6
Keyword clustering map. R&D, Research and Development; AI, Artificial Intelligence; S&T, Science and Technology; LDA, Latent Dirichlet Allocation.
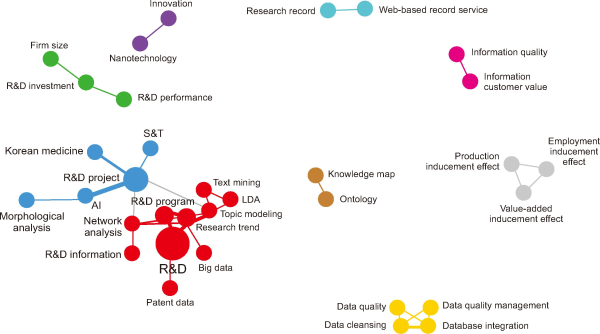
■ Cluster 1 (red): The largest cluster by keyword volume, links core R&D concepts (e.g., R&D information/project) with relevant data types (e.g., big data, patent data), advanced analytical methodologies (e.g., text mining, network analysis, topic modeling, LDA), and research goals like trend analysis, demonstrating their interconnectedness. Characteristically, studies within this cluster typically involve collecting datasets (papers, research projects, patent data) from sources such as NTIS, focusing on specific fields (e.g., autonomous driving, cloud security, immersive media), analyzing these data using various techniques, deriving research topics, and suggesting future research directions based on the findings. For instance, Woo and Lee (2020) applied LDA-based topic modeling to a Korean national R&D project dataset in the ICT sector to analyze key research topics related to intelligent information technology. Kim et al. (2023) compared research trends in the ICT field of South and North Korea by applying data mining methods. In another study representative of this cluster, Lee and Lee (2022) collected national R&D project data in the metaverse field to analyze temporal shifts in research themes.
■ Cluster 2 (blue): This is the second largest cluster. It primarily includes research focused on analyzing research trends in specific fields centered on R&D projects, as well as improving the NTIS search system using AI technologies or morphological analysis. Kwon et al. (2017) notably analyzed the public investment status in Korean medicine by utilizing NTIS data, aiming to support future strategic planning for Korean medicine R&D. Lee et al. (2020) proposed the design and implementation of an interactive search system that analyzes users’ input words or sentences morphologically and leverages the KoBERT model to better identify user search intent and provide more accurate search results within the NTIS system.
■ Cluster 3 (green): Comprising keywords such as R&D investment, R&D performance, and firm size, this cluster explores the relationship between R&D investment and outcomes, taking organizational scale into account. This cluster consists of literature that measures investment performance or efficiency at the national level, specific industries, or specific technology fields based on paper analysis or patent analysis using NTIS data. For example, Kim (2017) utilized NTIS data to evaluate the performance of government investment in national IT R&D from the perspectives of papers, patents, and commercialization, and proposed ways to improve investment efficiency and strategic budget allocation.
■ Cluster 4 (purple): Including keywords like nanotechnology and innovation, this cluster represents innovation studies within specific high-tech fields. This cluster primarily consists of papers that analyze the innovation characteristics of Korean government R&D investments using NTIS data, with a focus on the nanotechnology field. Lim et al. (2019) quantified the innovation characteristics of R&D investment in the nanotechnology field using data envelopment analysis (DEA). Lim and Kim (2020) identified innovation patterns by government departments using NTIS data on government R&D investment outcomes (papers, patents, revenue, employment, etc.) in the nanotechnology.
■ Cluster 5 (orange): With keywords such as database integration, data cleansing, data quality, and data quality management, this cluster addresses the dimensions of NTIS database management and data quality management. This cluster consists mostly of literature that suggested directions for database integration and data quality improvement during the initial construction phase of NTIS. After the mid-2010s, no further research has been conducted. Shon and Lim (2009) examined the integrated database construction and linkage methods for NTIS’s human resources, projects, and performance information. Shin et al. (2011) used NTIS as a case study to consider factors affecting data quality, such as quality policies, organization, business processes, and business rules.
■ Cluster 6 (brown): Featuring an ontology and knowledge map, this cluster focuses on methodologies for knowledge organization and visualization. The literature included in this cluster was conducted in the early to mid-2010s. These studies aimed to systematically structure national R&D information stored in NTIS using ontology and intelligent analysis techniques and to build knowledge map services, thereby enhancing the usability of NTIS data. Jeong (2015) developed a knowledge map service visualizing relationships between researchers, keywords, institutions, and journals by constructing a lightweight ontology and using topic modeling with national R&D data.
■ Cluster 7 (pink): Including information quality and information customer value, this cluster examines factors related to customer satisfaction and value in the context of NTIS services. This literature analyzed quality and customer value factors that influence customer satisfaction and user performance among users of the NTIS system, aiming to improve information service quality since the initial service provision phase. Suh et al. (2014) found that information service quality positively affects customer value and information source recognition, which influences usage performance, recommending service strategies through user analysis to enhance NTIS’s value.
■ Cluster 8 (gray): With keywords such as value-added inducement effect, production inducement effect, and employment inducement effect, this cluster analyzes the economic impacts resulting from NTIS. Park (2018) conducted an inter-industry analysis using the Bank of Korea’s input-output tables to analyze the economic ripple effects of NTIS. The results revealed substantial production-inducing effects, value-added effects, and employment-inducing effects compared to the government R&D budget investment, demonstrating the system’s socioeconomic contributions.
■ Cluster 9 (mint): Containing a research record and web-based record information service, this cluster addresses research documentation and the delivery of online information services. The literature in this cluster primarily consists of studies from the late 2010s that suggest directions for activating web-based research record information services centered on NTIS. Nam et al. (2017) developed evaluation indicators reflecting research record characteristics through service quality indicator analysis, applying these to NTIS as a case study to identify service problems and propose improvement measures for web-based research record information services.
In summary, the core themes of NTIS-related research converge on: data and system management, analysis of R&D investment and performance, enhancement of user value and analysis of economic ripple effects, and application of diverse analytical methodologies. These themes illuminate the multifaceted role of NTIS in promoting national R&D and innovation, alongside the development process of the NTIS system itself. Furthermore, synthesizing the thematic analysis of this study reveals that research related to Korea’s NTIS holds significant meaning beyond a simple exploration of knowledge structures. It serves as an important case from information science, sociological, and R&D policy perspectives, concretely demonstrating how national investment in R&D information infrastructure influences the generation, direction, and diversification of academic knowledge. In other words, this suggests that NTIS acts as a driver promoting the propagation and differentiation of various research topics within the academic ecosystem, moving beyond the mere role of an R&D information service provider.
5. CONCLUSIONS
5.1. Discussion
This study reveals that NTIS-related research has fundamentally shifted from system-oriented development toward broader scholarly application, demonstrating that NTIS is increasingly functioning as academic infrastructure within South Korea’s research landscape rather than merely serving as an information portal.
This comprehensive bibliometric analysis of NTIS-related academic literature in South Korea from 2008 to 2024 goes beyond simply quantifying a research area to demonstrate how national R&D information infrastructure dynamically co-evolves with its surrounding academic and policy ecosystems. Our findings provide insights into how such platforms both shape and are shaped by broader currents of governance, knowledge production, and technology adoption.
This study reveals that despite steady growth, the limited research volume coincides with pronounced institutional concentration around KISTI, the system development and operation entity. HHI analysis shows relatively low concentration in publications but higher concentration in citations, confirming that influential research clusters among specific institutions. This pattern reflects important dynamics: While KISTI’s central role has clearly driven knowledge production and established it as a hub in inter-institutional collaboration networks, it simultaneously fosters knowledge path dependency and tends to channel academic participation in specific directions. For NTIS to develop as a truly national research platform, gradual evolution is needed from the current supplier-centered model led by core operating institutions toward an expanded demand-driven ecosystem that actively embraces diverse perspectives from universities and other research disciplines.
Furthermore, changes in research themes reflect a significant transformation in South Korea’s national R&D paradigm. The decline in research focused on system development and data management, coupled with a surge in trend analysis and performance evaluation studies utilizing NTIS data, demonstrates that NTIS has matured beyond a simple information repository. Academic fields are also expanding significantly from traditional technology policy and library and information science to interdisciplinary research, business administration, and engineering domains. Nine thematic clusters identified through keyword cluster analysis concretely illustrate this diversification, particularly confirming that while R&D lifecycle-related terms maintain their central role across all periods, advanced analytical techniques such as big data, text mining, and AI are emerging as new research drivers. This transformation reflects the institutionalization of data-driven governance in S&T policy, positioning NTIS beyond simple service provision as a core tool for national innovation strategy. However, such changes bring new challenges. The relative decline of foundational disciplines such as library and information science and R&D policy, which traditionally provide theoretical foundations, may potentially weaken the long-term intellectual base for such applied research.
Finally, this analysis reveals important knowledge gaps that represent both challenges and opportunities for future research. The overwhelming domestic concentration of research leads to insufficient international comparative studies, and the pattern of publications centered on domestic journals limits the global dissemination of research outcomes. While the application of advanced analytical methods such as AI and text mining is increasing, in-depth research on national data governance, the specific impact of NTIS data on policy decisions, and the role of information science in shaping technology policy remains insufficient. Addressing these gaps is crucial. Through this, NTIS-related research can advance beyond its current focus on data utilization to develop as a core research area exploring the complex interactions among national R&D infrastructure investment, knowledge production dynamics, and policy innovation.
5.2. Practical Implications for Enhancing NTIS-Related Research
Our analysis reveals limited research volume (169 articles over 16 years) and pronounced institutional concentration around KISTI (37.3% of total publications), underscoring the urgent need to broaden participation beyond the current supplier-centered model. As practical measures, research support programs such as thesis competitions utilizing NTIS data or workshops for early-career researchers should be expanded, and regular NTIS-related sessions should be operated in collaboration with relevant academic societies to form a focal point for the researcher community. Additionally, efforts to plan and support interdisciplinary convergence research projects should be undertaken to accelerate the positive trend of research expansion into various fields such as business administration and engineering. In particular, while maintaining the current KISTI-centered research network, it is necessary to gradually expand participation from universities and private research institutions, promoting a transition from a supplier-centered to a demand-centered research ecosystem.
Thematic analysis demonstrates a concerning narrowing of focus toward data utilization, with such studies increasing by 42.6% while foundational system improvement research declined by 25.9%, pointing to the need for deeper theoretical engagement to strengthen the intellectual foundation. This trend shows that while NTIS data utilization research has increased quantitatively, it is concentrated on specific topics, and research addressing theoretical foundations has actually diminished. Therefore, it is necessary to establish and guide research agendas that can add depth to research from a long-term perspective, beyond short-term trend analysis. Specifically, research in technology policy and library and information science fields should be reactivated to strengthen the theoretical foundation of NTIS research, and exploration of challenging topics should be encouraged, including the knowledge gaps identified in this study: national data governance frameworks, evaluation of NTIS’s policy decision influence, and comparative studies with similar overseas systems. Additionally, empirical analysis of NTIS data’s role in evidence-based policy formation and its actual impact on the national innovation system, which are currently insufficient, should also be expanded.
The findings reveal overwhelming domestic concentration, with NTIS studies concentrated primarily within South Korean academic institutions and journals, and a notable absence of international comparative studies, indicating significant opportunities for global integration. To address this limitation, it is necessary to activate international comparative research and expand cooperation with overseas researchers. Through publishing NTIS special issues in international academic journals such as the Journal of Information Science Theory and Practice (JISTaP) or operating NTIS sessions at international academic conferences, South Korea’s experience with national R&D information systems can be shared with the international academic community. Such efforts will enable comparative analysis with similar systems in other countries and provide opportunities to objectively evaluate NTIS’s relative strengths and weaknesses.
The increasing use of advanced analytical methods, with AI, big data, and topic modeling emerging as dominant keywords, points to the need for NTIS to expand its data openness and technical capabilities to support sophisticated analytical approaches. Since the development of the research ecosystem directly depends on the platform’s openness and functionality, system innovation should be pursued for NTIS to leap beyond a domestic information service to become a global research infrastructure. To this end, compatibility with international standards should be secured by applying global identifiers and providing multilingual APIs to enhance accessibility for overseas researchers, and data sharing and reuse policies based on Open Science principles should be strengthened. Additionally, AI-based intelligent analysis functions should be introduced to seek evolution into a ‘knowledge discovery platform’ where researchers can discover new insights through data, beyond simple information retrieval. Development of customized services reflecting the requirements of various stakeholders including researchers, policymakers, industry, and the general public should be undertaken, along with continuous improvement through regular user experience evaluations.
5.3. Contributions and Limitations
This study makes a major contribution by expanding the academic scope of existing quantitative bibliometric analysis, which had been limited to specific technologies or academic fields, to a national R&D information system (NTIS) itself. Through this approach, the study systematically identifies the unique characteristics and developmental process of the NTIS system, as well as its associated research landscape and knowledge structure. Furthermore, it contributes to laying a foundation for future research on similar R&D information systems or platforms by integrating bibliometric, network, thematic analysis, and selective review methods. This study also makes a significant academic contribution by empirically demonstrating that NTIS has evolved beyond a simple information provider into a core academic infrastructure for data-driven research, and by clarifying the process through which a national information infrastructure influences the direction and form of academic knowledge production. Based on the diversification of research topics, the expansion of academic fields, and the sophistication of analytical methodologies, the study identifies that NTIS functions not merely as an information repository but as a driving force that promotes and differentiates research across various disciplines. This study further contributes from a policy and practical standpoint by diagnosing the inherent limitations of an academic field centered on a specific information system and proposing practical directions for overcoming them. By addressing problems such as a quantitative lack of research, knowledge production centered on specific institutions, and a research scope limited to domestic boundaries, the study proposes concrete strategies, including the vitalization of research communities, diversification of research areas, global expansion through international collaborative research, and strengthening of inter-institutional cooperation. Through these proposals, the study provides important policy implications for the sustainable development of national R&D information infrastructures, including NTIS.
While this study provides comprehensive insights into NTIS-related research patterns, several methodological constraints and scope limitations inevitably influence our findings and their broader applicability. The most fundamental limitation stems from our exclusive analysis of Korean literature, which, while providing deep understanding of the domestic research landscape, constrains our ability to position NTIS within the broader international context of national R&D information systems. This domestic-focused perspective limits our understanding of whether the observed patterns represent universal tendencies in national R&D information ecosystems or reflect Korea-specific developmental trajectories. Furthermore, the methodology applied in this study was effective in systematically analyzing research trends and collaboration patterns, but has limitations in capturing the substantial impact of NTIS on the academic ecosystem—namely, the deeper mechanisms such as actual policy decision processes or new R&D project planning. While our bibliometric analysis successfully identified macroscopic knowledge structure patterns, it could not elucidate the complex mechanisms through which NTIS data has specifically influenced R&D policy-making processes, national innovation systems, and academic communities. This gap between observable publication patterns and actual impact on the academic-policy ecosystem represents a significant constraint in fully assessing NTIS’s role as policy infrastructure. Moreover, the selective literature review approach employed in this study, while offering the advantage of providing qualitative insights into major research themes, operates within the constraints of subjective judgment rather than systematic synthesis. Although this approach enabled us to capture in-depth analysis of research focus areas, it lacks the methodological rigor that systematic literature review methods can provide.
These limitations collectively point toward promising directions for future research. International comparative studies examining multiple national R&D information systems, including the United States RePORTER and Japan’s KAKEN, would provide crucial context not only for interpreting the Korean experience but also for understanding within a global framework. Mixed-methodological approaches combining bibliometric analysis with surveys and case studies could bridge the gap between observable publication patterns and actual impact on the academic ecosystem. In particular, the application of systematic literature review methodologies would enable more rigorous and structured synthesis of research methodologies, research topics, and results, supporting clearer judgments about the relative importance of different research streams.
REFERENCES
(2016) Differing disciplinary citation concentration patterns of book and journal literature? Journal of Informetrics, 10, 814-829 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2016.05.005.
, (2022) Determinants of continuous intention-to-use on NTIS: Perspectives of UTAUT and TTF Model The Journal of Information Systems, 31, 197-216 https://doi.org/10.5859/KAIS.2022.31.2.197.
, , , (2021) Exploring the knowledge structure of fuel cell electric vehicle in national R&D projects for the hydrogen economy The Journal of the Korea Contents Association, 21, 306-317 https://doi.org/10.5392/JKCA.2021.21.06.306.
, (2020) A study on the characteristics of R&D for technology development in Chungbuk area : Focused on text analysis and network analysis Journal of Industrial Innovation, 36, 1-19 https://doi.org/10.22793/indinn.2020.36.2.001.
, , , , (2021) How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines Journal of Business Research, 133, 285-296 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.04.070.
European Commission (EC) (n.d.) Community Research and Development Information Service (CORDIS) https://cordis.europa.eu Article Id (other)
, , , (2021) Some dominance indices to determine market concentration Journal of Applied Statistics, 48, 2755-2775 https://doi.org/10.1080/02664763.2021.1963421. Article Id (pmcid)
, (2020) An inductive study on the service quality evaluation model of online information service : Focusing on the national online information service NTIS and NDSL Journal of Information Technology Services, 19, 71-87 https://doi.org/10.9716/KITS.2020.19.1.071.
(2005) An index to quantify an individual's scientific research output Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 102, 16569-16572 https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507655102. Article Id (pmcid)
, , , (2009) An economic feasibility analysis on the establishment of dedicated management system for the national R&D reports Journal of the Society of Korea Industrial and Systems Engineering, 32, 45-56 https://www.kci.go.kr/kciportal/ci/sereArticleSearch/ciSereArtiView.kci?sereArticleSearchBean.artiId=ART001353679. Article Id (other)
, , , (2022) Changes in the structure of collaboration network in artificial intelligence by national R&D stage Journal of Information Science Theory and Practice, 10, 12-24 https://doi.org/10.1633/JISTaP.2022.10.S.2.
Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) (n.d.) Grants-in-aid for scientific research https://www.jsps.go.jp/english/e-grants/ Article Id (other)
(2015) A study on ontology and topic modeling-based multi-dimensional knowledge map services Journal of Intelligence and Information Systems, 21, 79-92 https://doi.org/10.13088/jiis.2015.21.4.079.
(2017) Performance evaluation of national R&D investment in information technology areas Journal of The Korea Society of Computer and Information, 22, 119-125 https://doi.org/10.9708/jksci.2017.22.02.119.
, , (2023) A comparative analysis of research trends in the information and communication technology field of South and North Korea using data mining Journal of Information Science Theory and Practice, 11, 14-30 https://doi.org/10.1633/JISTaP.2023.11.1.2.
, (2025) Exploring and comparing the knowledge structures, collaborations and key themes of electric vehicle research in the environment domain International Journal of Sustainable Transportation, 19, 195-210 https://doi.org/10.1080/15568318.2024.2448002.
, , , (2016) Analysis of the determinants influencing technology transfer in government funded research institutes: Focusing on features of national R&D projects The Journal of the Korea Contents Association, 16, 624-639 https://doi.org/10.5392/JKCA.2016.16.08.624.
Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information (KISTI) (n.d.) NTIS introduction https://www.ntis.go.kr/ThAbout.do Article Id (other)
, , , , (2022) A study on research support service of the national R&D full cycle Journal of the Korean Society for Library and Information Science, 56, 405-423 https://doi.org/10.4275/KSLIS.2022.56.1.405.
, , , (2017) The recent trend of R&D investment in Korean medicine by research steps and fields Journal of Society of Preventive Korean Medicine, 21, 69-78 https://doi.org/10.25153/spkom.2017.21.2.008.
, (2021) Information analysis framework for supporting evidence-based research and development policy: Practical considerations for rationality in the policy process Informatization Policy, 28, 77-93 https://doi.org/10.22693/NIAIP.2021.28.1.077.
, (2022) An analysis of national R&D trends in the metaverse field using topic modeling Smart Media Journal, 11, 9-20 https://doi.org/10.30693/SMJ.2022.11.8.9.
, , (2022) Design and implementation of an interactive search system based on KoBERT Journal of Knowledge Information Technology and Systems (JKITS), 17, 1081-1088 https://doi.org/10.34163/jkits.2022.17.5.028.
, , (2020) Design and implementation of interactive search service based on deep learning and morpheme analysis in NTIS system Journal of Convergence for Information Technology, 10, 9-14 https://doi.org/10.22156/CS4SMB.2020.10.12.009.
, (2021) A study on provision of national R&D information: Perspective of research conducting institutions Journal of D-Culture Archives, 4, 149-158 https://doi.org/10.23089/jdca.2021.4.1.010.
, , , (2008) Using patent information for designing new product and technology: Keyword based technology roadmapping R&D Management, 38, 169-188 https://www.scilit.com/publications/393a2cf0b761f72cc4ade915fa45876e. Article Id (other)
, (2020) Quantifying innovation characteristics of national R&D investment through cross-cutting data analysis : Case study on NTIS nanotechnology Journal of The Korean Operations Research and Management Science Society, 45, 13-23 https://doi.org/10.7737/JKORMS.2020.45.2.013.
, , , (2019) Study on innovation measurement of national R&D investments for nanotechnology using data envelopment analysis Journal of Korea Technology Innovation Society, 22, 207-219 https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO201919867048948.page. Article Id (other)
, , , (2024) Classification of strategy types for global R&D collaboration: An analysis of Korea's partnerships with developing countries Journal of Climate Change Research, 15, 1085-1098 https://doi.org/10.15531/KSCCR.2024.15.6.1085.
, , (2017) Developing and applying the evaluation measures for web based information services of research records archives - focused on NTIS - Journal of Korean Library and Information Science Society, 48, 345-372 https://doi.org/10.16981/kliss.48. .
National Institutes of Health (NIH) (n.d.) Research Portfolio Online Reporting Tools, Expenditures, and Results (RePORTER) https://reporter.nih.gov Article Id (other)
National Institute of Informatics (NII) (n.d.) KAKEN database https://kaken.nii.ac.jp/en Article Id (other)
(2008) Comparative analysis of R&D information status: Korea, US, and Japan Journal of the Korean Society for Library and Information Science, 42, 207-231 https://doi.org/10.4275/KSLIS.2008.42.3.207.
, (2020) The effect of government R&D support for middle-sized firm Productivity Research: An International Interdisciplinary Journal, 34, 231-257 https://www.kci.go.kr/kciportal/ci/sereArticleSearch/ciSereArtiView.kci?sereArticleSearchBean.artiId=ART002573200. Article Id (other)
(2008) An analysis of economic effect of national knowledge information system development Journal of Information Science Theory and Practice, 39, 73-94 https://www.kci.go.kr/kciportal/ci/sereArticleSearch/ciSereArtiView.kci?sereArticleSearchBean.artiId=ART001282585. Article Id (other)
(2018) An economic ripple effect analysis of national science & technology information service : Focusing an input-output analysis Journal of Korea Technology Innovation Society, 21, 1296-1312 https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO201819867049447.page. Article Id (other)
, , , , (2012) A study on models of economic performance analysis for science and technology information management distribution project Journal of Information Management, 43, 43-59 https://doi.org/10.1633/JIM.2012.43.3.043.
, , (2018) A study on the performance of the Korean government R&D investment in the area of industrial technology Journal of Industrial Innovation, 34, 163-189 https://doi.org/10.22793/indinn.2018.34. .
, , , , (2011) A data cleansing strategy for improving data quality of national R&D information - case study of NTIS Journal of The Korea Society of Computer and Information, 16, 119-130 https://doi.org/10.9708/jksci.2011.16.6.119.
, , , , , (2022) Open Science-friendly national R&D knowledge and information infrastructure: A case study from Korea Septentrio Conference Series [1] https://doi.org/10.7557/5.6591.
, (2009) Research of quality improvement by factors analysis data quality problem: Focus on national R&D information linking structure The Journal of the Korea Contents Association, 9, 1-14 https://doi.org/10.5392/JKCA.2009.9.1.001.
(2019) Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines Journal of Business Research, 104, 333-339 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.039.
, , (2014) Factors influencing the customer value and the performance of national R&D information services of the R&D managers The Journal of the Korea Contents Association, 14, 480-494 https://doi.org/10.5392/JKCA.2014.14.07.480.
, , (2019) From Louvain to Leiden: Guaranteeing well-connected communities Scientific Reports, 9, 5233 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41695-z. Article Id (pmcid)
, , (2023) Case studies and a taxonomy of science of STI policy programs for exploring the evidence-based approach Innovation Studies, 18, 63-96 https://doi.org/10.46251/INNOS.2023.2.18.1.63.
, (2020) Investigation of research topic and trends of national ICT research-development using the LDA model Journal of the Korea Convergence Society, 11, 9-18 https://doi.org/10.15207/JKCS.2020.11.7.009.
, , , (2020) Feature analyze and research of national convergence R&D: With focus on the text mining Journal of Information Technology Applications and Management, 27, 59-73 https://doi.org/10.21219/jitam.2020.27.1.059.
, , , , (2018) Exploring the dynamic knowledge structure of studies on the Internet of things: Keyword analysis ETRI Journal, 40, 745-758 https://doi.org/10.4218/etrij.2018-0059.
, , (2020) Curation service to improve user's access to national R&D information : Focusing on issues R&D service The Journal of the Korea Contents Association, 20, 1-10 https://doi.org/10.5392/JKCA.2020.20.09.001. Article Id (other)
- Received
- 2025-04-01
- Revised
- 2025-07-03
- Accepted
- 2025-07-14
- Published
- 2025-09-30
- Downloaded
- Viewed
- 0KCI Citations
- 0WOS Citations