Vol.13 No.2
Abstract
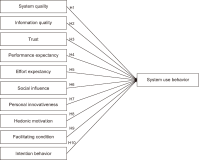
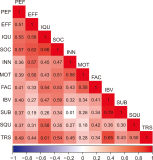
This study examines factors influencing the use of recommendation systems for elderly research in Thailand through a quantitative research design. The target population comprises researchers experienced in elderly studies from 2012 to 2022, totaling 348 participants. Data were collected via a validated questionnaire (Cronbach’s alpha=0.955). Employing an extended the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology 2 model, the study investigates system use behavior (SUB) based on seven core factors: Performance expectancy (PEF), effort expectancy (EFF), social influence, personal innovativeness (INN), hedonic motivation (MOT), facilitating conditions (FAC), and intention behavior (IBV), alongside three additional factors—system quality (SQU), information quality (IQU), and trust. Multiple correlation and regression analyses reveal statistically significant influences (p<0.05) from eight factors. SQU, PEF, EFF, MOT, FAC, and IBV positively influence SUB. Conversely, IQU and INN negatively affect system usage. The predictive model is expressed as: SUB=1.195+0.116 (SQU)-0.268 (IQU)+0.134 (PEF)+0.181 (EFF)-0.406 (INN)+0.137 (MOT)+0.097 (FAC)+0.866 (IBV). These findings underscore the importance of optimizing system features and recognizing the distinct needs and expectations of elderly research communities to enhance the effectiveness of these recommendation systems.

Abstract
This study addresses information management and absorptive capacity in the context of open innovation projects—essential topics for public and private organizations. The construction of the conceptual model is based on the consolidated literature on these topics, also incorporating recent empirical studies that highlight their complementarity and confirm existing gaps in the area. The proposed theoretical model considers the stages of innovation development, represented by the innovation funnel, integrating the information process model and the absorptive capacity model. The proposed model aims to support managers in systematizing the innovation process, using information as a foundation for absorptive capacity and promoting the integration of information management, absorptive capacity, and open innovation. The implementation of open innovation can be carried out through the effective management of information flow and the application of new knowledge, facilitating decision-making and enhancing innovation outcomes. It is expected that this study will contribute to the advancement of these topics and offer practical instruments that strengthen the agenda of innovation managers.

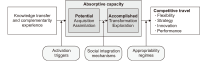

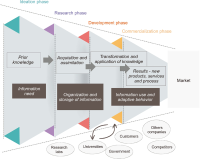
Abstract
This study investigates the practices of Western YouTube content creators’ cross-posting behavior, i.e., uploading their content on Bilibili—a Chinese video-sharing platform. A qualitative content analysis is employed to analyze videos of 14 popular YouTubers to compare the content of videos posted on both platforms. The findings indicate that the content differs for both platforms, possibly to accommodate Chinese viewers. The results show that Western YouTubers have made multiple changes to their original content before reuploading them to Bilibili, including the addition of Chinese subtitles, cut-out sponsorship content, shorter and translated descriptions, altered thumbnails, and exclusive content for Bilibili. The results also show a less frequent uploading schedule on Bilibili than on YouTube. While existing studies have explored content creators’ cross-posting behavior within the same social media ecosystem, the study significantly contributes to advancing our understanding of online creators’ content distribution practices across platforms in different cultural domains, especially in a Chinese-Western context.


Abstract
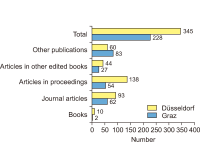
Many descriptions and evaluations of research institutions apply publication and citation indicators, which can also be found in most of the popular rankings of universities all over the world. When comparing different institutions, the question arises whether scientometric indicators, and institutional rankings derived from them, are really valid. In our paper we discuss various dimensions of scientometric analyses which have a more or less strong impact on the results of research evaluations on the scientometric meso-level (e.g., department or university level). Concerning research output (based upon publications), we found nine different dimensions, namely time period, size of the institution, representatives of the institution, data source, language, document types and their weighting, co-authorship, document length, and access option. Concerning research impact (based upon citations), there are 14 different dimensions. Using the simple example of two university departments, we present different rankings while varying a few attributes of the suggested dimensions. As the results show, there are large differences between the performed rankings. Each ranking stresses a different aspect; hence there is not the one and only valid ranking. All the popular global university rankings work with arbitrary selections of indicator combinations, making the results more or less arbitrary. The greatest issues are the rankings’ incomplete empirical bases, the non-consideration of fractional counting of authors, and – most importantly – the disregarding of the institutions’ sizes.

Abstract
Augmented reality (AR) offers significant potential for inclusive design by merging virtual and physical environments to support equitable interaction and engagement. This study explores the role of AR in facilitating inclusive play, focusing on how it can enhance information accessibility and collaboration among children with and without disabilities. Using participatory design methodologies, we engaged 21 children aged 8-13, including children with and without disabilities, in co-design sessions to identify barriers and opportunities within AR-based activities. The study included both online and offline sessions, ensuring diverse participation and perspectives. We employed a thematic analysis approach to examine patterns in children’s interactions with AR, focusing on engagement, accessibility, and collaborative play. Findings reveal that AR can blur social and physical barriers, foster engagement through interest-driven interaction, and provide adaptive tools to support diverse user needs. The study also highlights the importance of autonomy, tailored technological support, and the role of facilitators in designing equitable AR environments. By positioning AR as a tool for inclusivity, this research contributes to the broader field of information science, offering insights into designing systems that prioritize information accessibility, user engagement, and collaborative interaction. Practical implications for developing AR-based information systems and environments are discussed.




Abstract
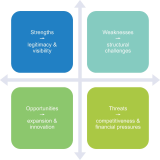
The current state of scholarly publishing is marked by the dominance of commercial publishers, the expansion of open access (OA) models, and the persistent challenges faced by independent, non-commercial journals. The aim of this paper is to critically examine the 12-year developmental course of the Journal of Information Science Theory and Practice (JISTaP), analyzing how an Asia-based library and information science journal with global aspirations has navigated academic publishing challenges. By tracing four distinct developmental epochs from 2013 to the present, the research explores its adaptation strategies, institutional support mechanisms, and bibliometric performance. An analysis of publication trends and citation patterns revealed significant growth, with steady increases in submissions and published articles despite systemic challenges for independent journals. A strengths–weaknesses–opportunities–threats analysis identified JISTaP’s key strengths, including robust institutional support from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information (KISTI) and an innovative OA model. However, critical challenges remain, such as limited Social Sciences Citation Index visibility and modest citation impact. The findings illuminate external pressures confronting non-commercial scholarly journals, including predatory publishing threats, technological disruptions, and the emerging complexities of AI-driven editorial systems. This research presents JISTaP’s 12-year trajectory as a critical case study of how a scholarly journal from an underrepresented region can strategically navigate global scholarly communication barriers, demonstrating that success lies in reimagining academic influence through institutional support, digital innovation, and a commitment to OA principles that transcend commercial publishing constraints.