Latest Articles
Vol.13 No.3
6papers in this issue.

Abstract
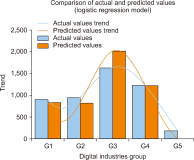
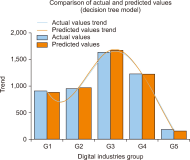
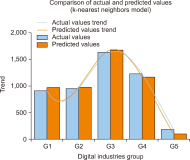
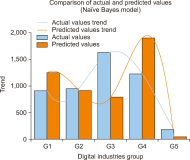
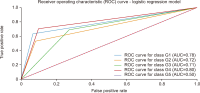
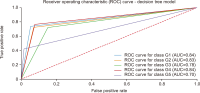
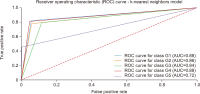
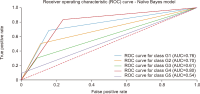
Thailand’s digital industry is experiencing rapid growth, driven by government initiatives and the widespread adoption of digital technologies. In response to this dynamic development, the present study proposes a predictive model to forecast future workforce requirements across five key segments of the digital industry: hardware and smart devices, software and software services, digital services, digital content, and telecommunications. Data were collected via web scraping from ten job advertisement websites between 2023 and 2024, resulting in a dataset comprising 24,494 job positions. The collected data underwent comprehensive preprocessing through natural language processing techniques—including text cleaning, punctuation removal, tokenization, stop word removal, and feature extraction using term frequency-inverse document frequency—to prepare it for analysis. Four supervised machine learning models (logistic regression, decision tree, k-nearest neighbors, and Naïve Bayes) were constructed and evaluated using performance metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, alongside receiver operating characteristic-area under the curve analysis. The results demonstrate that the k-nearest neighbors model outperformed the other methods, achieving an accuracy (AUC) of 0.792, precision of 0.793, recall of 0.731, and an F1-score of 0.751, with all models yielding AUC values greater than 0.5. These findings indicate an upward trend in digital service job demand and underscore the model’s potential utility in guiding workforce planning and human resource strategies in the digital sector. The study offers a robust, data-driven framework that can be adapted to forecast workforce needs in other rapidly evolving industries.

Abstract
This study employed a convergent mixed-methods approach to examine the development of learning communities among longan farmers in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand, and the role of information professionals in community engagement. Quantitative and qualitative data were collected simultaneously and synthesized to provide a comprehensive understanding. The qualitative phase involved structured interviews with ten longan farmers, with six participating, and data were analyzed descriptively to assess learning community development. In the quantitative phase, surveys were distributed to 144 stakeholders, with 136 completed responses (94.44%). Descriptive and inferential statistical analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS Statistics 30.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA), including the Shapiro-Wilk test, Friedman test, and Wilcoxon Signed-Rank test, to evaluate the significance of community engagement in agricultural development. Findings from the qualitative analysis highlight three key aspects of learning center operations: (1) management, (2) farmer skills development, and (3) knowledge creation and transfer. The quantitative results identify four areas in which information professionals contribute to community engagement: (1) Outreach (Information Providing), (2) Collaboration (Information Evaluation), (3) Involvement (Information Analysis), and (4) Consultation (Information Consulting). Qualitative insights complement the statistical findings, providing a deeper understanding of the learning community development process. This integration clarifies the role of information professionals and supports policy development initiatives aimed at strengthening the agricultural capacity of longan farmers, with potential applicability to other agricultural communities. Furthermore, the study offers a framework for information professionals, librarians, and agricultural specialists to enhance learning communities and contributes to the advancement of curricula in library and information science.



Abstract
This research analyzes and develops an essential dataset for creating a community information system (CIS) for managing cultural capital. The study has three primary objectives: (1) to identify and define key data categories required for a CIS focused on cultural capital management; (2) to assess the relevance and necessity of each data category through expert evaluation, particularly from individuals with practical experience in utilizing cultural capital in communities; and (3) to propose a dataset that can be adopted by local administrative organizations in Thailand to support cultural capital management and policy-making. The methodology employed in-depth interviews with six key informants: two cultural practitioners from local administrative organizations, two experts in dataset development, one expert in arts, culture, and local wisdom, and one user of cultural data for professional, educational, or research purposes. Data were analyzed using content analysis to identify standardized datasets, based on concepts of CIS, cultural capital information, and datasets, with verification through triangulation. Findings revealed that the essential data for developing the community cultural capital information system comprises two main datasets: community data, consisting of 117 data points with an overall high necessity rating, and cultural capital data, comprising 127 data points with an overall very high necessity rating. These findings establish the crucial data required for effective utilization of the system in managing cultural capital at the community level.


Abstract
The rising volume of electronic waste generated by public organisations in the Thi-Qar province of Iraq adversely affects the environment due to inadequate recycling and disposal methods, thereby intensifying pressures on enterprises. This research seeks to identify the factors influencing organisational managers’ adoption of environmentally sustainable e-waste disposal methods. A research model was established to connect three components: coercive pressure, normative influence, and mimicry. It investigates the impact of adopting environmentally responsible e-waste disposal and analyses the mediating role of attitude. The model underwent validation through data collected from a field survey involving 302 managers of public organisations in the Thi-Qar province. A questionnaire was created to gather data, consisting of five primary variables represented by twenty-one items. The seven-dimensional scalar form was employed for measurement and underwent reliability and validity assessments. Partial least squares were utilised to analyse the survey responses. The findings demonstrated that coercive, mimetic, and normative pressures significantly influenced attitudes and the adoption of environmentally responsible e-waste disposal practices. Attitudes regarding the environmental disposal of e-waste influence the adoption of eco-friendly disposal methods and mediate the effects of coercive, mimetic, and normative pressures on this adoption. This study advances the green information technology literature by identifying critical institutional factors influencing environmental behaviour and provides practical recommendations for policymakers and organisations to improve e-waste management strategies.


Abstract
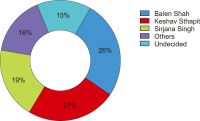
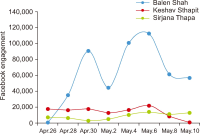
As political engagement is increasingly migrating to social media platforms, understanding the emotional dynamics embedded in online reactions has become critical to interpreting voter behavior. This study explores how Facebook’s reactions function as affective signals of voter sentiment and predictive indicators of electoral outcomes, using the 2022 Kathmandu metropolitan mayoral election. Drawing on emotion theory and affective information behavior, the research analyzes 322 Facebook posts related to the campaign from three leading candidates: Balen Shah, Keshav Sthapit, and Sirjana Singh, focusing on emoji-based reactions, shares, and comments. Sentiment scores were computed using a weighted classification of emojis, and predictive potential was assessed through rank-order analysis and correlation with actual vote shares. The result reveals a positive correlation between preelection sentiment indicators and electoral outcomes. Balen Shah, who led in both emotional engagement and final vote count, demonstrated how affective online support can signal electoral strength. Time-truncation and unweighted scoring further validated the robustness check. Additionally, text analytics highlight Shah’s resonance with majority voters and his alignment with calls for systemic change, contrasting with mixed sentiment toward the latter two. This study contributes to the growing literature on digital political engagement by demonstrating that emoji reactions can serve as reliable proxies for public sentiment in emerging democracies. The findings suggest practical implications for political strategists, campaign managers, and communication agencies seeking to understand and respond to digital sentiment in real time.



Abstract
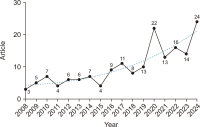
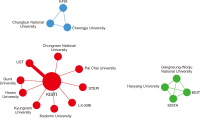
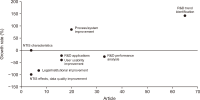
This study represents the first systematic analysis of research related to the National Science & Technology Information Service (NTIS)—South Korea’s comprehensive national Research and Development (R&D) information portal—from 2008 to 2024, utilizing bibliometric analysis, thematic analysis, and selective literature review. The study aims to identify key research trends, collaborative patterns, and thematic evolution in NTIS-related research to understand its knowledge structure and provide directions for scholarly and system development. The analysis reveals that despite limited publications (169 articles), NTIS research demonstrates steady growth with 13.9% annual growth. Distribution analysis using Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) indicates low concentration levels across authors, institutions, and journals, though citations show higher concentration. Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information (KISTI) leads in all performance indicators and serves as the central hub in interinstitutional collaboration networks. Research scope has expanded into diverse academic fields, with growth in interdisciplinary studies, business administration, and engineering. While studies using NTIS data have increased, research on system improvement has declined. Thematic evolution analysis reveals nine research clusters and shows a shift from system development towards R&D trend analysis, performance evaluation, and advanced analytical methodologies, including Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies. Major research themes include NTIS system implementation, data quality management, R&D investment-performance analysis, economic impact assessment, and analytical techniques. This study indicates that NTIS’s function is evolving beyond R&D information service into a data-driven academic analysis infrastructure supporting evidence-based knowledge production across disciplines. To address limited research volume and domestic concentration, this study recommends activating NTIS-related academic communities, expanding international participation through compatibility with global systems, and building an intelligent platform for customized services.